Abstract
The BET family proteins consist of BRD2, BRD3, BRD4 and BRDT, with each of these proteins containing two highly conserved bromodomains (BDI and BDII). First generation BET inhibitors, including ABBV-075, are pan-BET inhibitors that bind with nearly equimolar affinity to BDI and BDII. Pan-BET inhibitors generally block transcription and inhibit the proliferation of a large spectrum of tumor types, but exhibit a narrow therapeutic index. ABBV-744 is a highly selective inhibitor for the BDII of BET family proteins, exhibiting greater than 300-fold more potent binding affinity to the BDII bromodomain of BRD4 relative to BDI (Warren Kati AACR 2018; Xiaoyu Lin AACR 2018). In this study, we evaluated the anti-leukemia activities of ABBV-744 in acute myelogenous leukemia (AML) cell lines and primary samples.
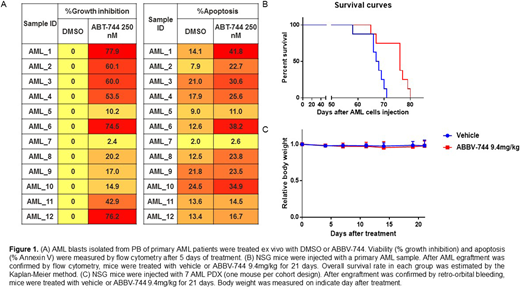
In AML cell lines, ABBV-744 induced G1 cell cycle arrest and apoptosis with caspase-3 activation and PAPR cleavage through regulation of the key proteins that are involved in cell cycle and apoptosis pathways (e.g. (BCL-2, BCL-XL, MCL-1, c-Myc). Mechanistically, ABBV-744 displaced BRD4 from the regulatory region of BCL2, RUNX1, BCL2L1 and IL8 genes by ChiP-Seq. MLL-rearranged cells were most sensitive to BDII inhibition, and ABBV-744 displaced both, BRD4 and MLL from the regulatory regions of BCL2 and c-Myc genes in MV4;11 (MLL-AF4) and Nomo-1 (MLL-AF9) cells. We examined anti-leukemia activity of ABBV-744 in 12 primary AML samples with diverse genetic alterations. ABBV-744 inhibited cell growth in 8/12 primary samples (20.2%-77.9%) and induced apoptosis (26.7 ± 9.6% in ABBV-744 group vs 14.1± 3.9% in DMSO group, p=0.007, Fig 1A). We next performed the whole genome transcriptome analysis of pre-treatment AML cells by RNA-sequencing (RNA-seq). The samples which were sensitive to ABBV-744 tend to have higher pro-apoptosis (TXNIP, DR5) and lower anti-apoptosis (BCL2, EXPO) than resistant samples.
For efficacy assessment in vivo, we established a patient-derived xenograft (PDX) from an AML patient with FLT3-ITD, DNMT3A, IDH1 and NPM1 mutations in NSG mice. Upon engraftment, mice were randomized to receive vehicle or single agent ABBV-744 at a well-below MTD dose of 9.4 mg/kg for 21 days. The median survival time of mice treated with ABBV-744 (Median survival: 76 days) was significantly higher compared to untreated mice (Median survival: 67.5 days, p=0.007, Fig 1B). Next, the anti-leukemia efficacy of ABBV-744 was tested in 7 additional AML PDX models. NSG mice were injected with 7 AML PDX (one mouse per cohort design). After engraftment was confirmed by retro-orbital bleeding, mice were treated with vehicle or ABBV-744. Circulating tumor burden was measured by flow cytometry in peripheral blood samples from mice collected on indicated days of therapy. In five of the 7 models, ABBV-744 treatment delayed AML progression compared to untreated mice (survival days: 135 vs 105, 205 vs 153, 62 vs 46, 118 vs 77, 97 vs 86). No significant impact on mice' weight was noted (Fig 1C), and no clinical signs of toxicity recorded over the course of therapy.
In summary, blockade of BET family bromodomain BDII promotes apoptotic cell death and suppresses proliferation in the majority of primary AML cells. Importantly, ABBV-744 therapy reduced AML tumor burden and extended survival in AML PDX models at a well-below MTD dose. Together, these results provide proof of concept that highly selective inhibitors of the second bromodomain of BET family may maintain robust anti-leukemia efficacy in AML while exhibiting improved tolerability relative to pan-BET inhibitors.
Uziel:AbbVie Inc.: Employment. Shen:AbbVie Inc: Employment. Konopleva:Stemline Therapeutics: Research Funding. Lin:AbbVie Inc: Employment. Lu:AbbVie Inc: Employment. Zhang:AbbVie Inc: Employment.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal